 PARP Research Group
PARP Research Group
 PARP Research Group PARP Research Group |
Universidad de Murcia  |
Projective Geometry
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Functions | |
| bool | computeFundamentalMatrix (const QVector< QPointFMatching > &matchings, QVMatrix &F, const TQVSVD_Method svdMethod=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Obtains the fundamental matrix between two images using the 8-point algorithm. | |
| double | symmetricEpipolarDistance (const QVMatrix &F, const QPointFMatching &matching) |
| Evaluate symmetric epipolar error for a fundamental matrix defined between two images and one image point correspondence. | |
| QVVector | symmetricEpipolarDistance (const QVMatrix &F, const QVector< QPointFMatching > &matchings) |
| Evaluate symmetric epipolar errors for a fundamental matrix defined between two images and a list of image point correspondences. | |
| bool | computeProjectiveHomography (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings, QVMatrix &H) |
| Obtains a planar homography from a list of point correspondences. | |
| QVMatrix | computeProjectiveHomography (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings) |
| Obtains a planar homography from a list of point correspondences. | |
| QVMatrix | computeAffineHomography (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings) |
| Obtains an affine homography from a list of point correspondences. | |
| QVMatrix | computeSimilarHomography (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings) |
| Obtains a similar homography from a set of inter-image point matchings. | |
| QVMatrix | cvFindFundamentalMat (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings) |
| Obtains the fundamental matrix between two images, using the 8 point algorithm. | |
| QPointF | applyHomography (const QVMatrix &homography, const QPointF &point) |
| Maps a point using an homography. | |
| QList< QPointF > | applyHomography (const QVMatrix &homography, const QList< QPointF > &sourcePoints) |
| Maps a set of points using an homography. | |
| QVImage< uChar, 1 > | applyHomography (const QVMatrix &homography, const QVImage< uChar, 1 > &image, const int interpolation=IPPI_INTER_CUBIC) |
| Performs an homography distortion on an image. | |
| QVImage< uChar, 3 > | applyHomography (const QVMatrix &homography, const QVImage< uChar, 3 > &image, const int interpolation=IPPI_INTER_CUBIC) |
| Performs an homography distortion on an image. | |
| void | getCameraPosesFromEssentialMatrix (const QVMatrix &E, QVMatrix &R1, QVMatrix &R2, QV3DPointF &t) |
| Decomposes an essential matrix and obtains the corresponding pair of camera poses. | |
| bool | testCheiralityForCameraPoses (const QVMatrix &sourceRt, const QPointF &sourceProjection, const QVMatrix &destRt, const QPointF &destProjection) |
| Tests if two camera poses satisfy the cheirality condition for the reconstruction of a 3D point. | |
| QVMatrix | linearCameraResection (const QList< QPointF > &points2d, const QList< QV3DPointF > &points3d) |
| Obtains the camera matrix from a set of correspondences between 3D points and their respective image projections. | |
| QV3DPointF | linear3DPointTriangulation (const QVector< QVMatrix > &cameraMatrices, const QHash< int, QPointF > &projectionsOfAPoint, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on several views, and their corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QV3DPointF | linear3DPointTriangulation (const QList< QVMatrix > &cameraMatrices, const QList< QPointF > &projectionsOfAPoint, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on several views, and their corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QV3DPointF | linear3DPointTriangulation (const QPointF &point1, const QVMatrix &P1, const QPointF &point2, const QVMatrix &P2, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QV3DPointF | linear3DPointTriangulation (const QPointFMatching &matching, const QVMatrix &P1, const QVMatrix &P2, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QV3DPointF | linear3DPointTriangulation (const QPointFMatching &matching, const QVCameraPose &pose1, const QVCameraPose &pose2, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QList< QV3DPointF > | linear3DPointsTriangulation (const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > &cameras, const QList< QHash< int, QPointF > > &pointProjections, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QList< QV3DPointF > | linear3DPointsTriangulation (const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > &cameras, const QVector< QHash< int, QPointF > > &pointProjections, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QList< QV3DPointF > | linear3DPointsTriangulation (const QList< QVCameraPose > &cameras, const QList< QHash< int, QPointF > > &pointProjections, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices. | |
| QList< QV3DPointF > | linear3DPointsTriangulation (const QList< QVCameraPose > &cameras, const QVector< QHash< int, QPointF > > &pointProjections, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices. | |
| bool | getCameraFocals (const QList< QPointFMatching > &matchings, double &focal1, double &focal2, const QPointF principalPoint1=QPointF(0.0, 0.0), const QPointF principalPoint2=QPointF(0.0, 0.0), const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType gslMinimizerAlgorithm=VectorBFGS, const int optimizationIterations=50) |
| Estimates the focal lengths for two cameras,. | |
| double | computeCameraFocalFromPlanarHomography (const QVMatrix &H, int w, int h, bool byzero=false) |
| Compute camera focal from a planar homography. | |
| QVCameraPose | getCameraPoseFromCalibratedHomography (const QVMatrix &K, const QVMatrix &H) |
| Estimates the camera pose form the intrinsic calibration and a planar homography. | |
| QVEuclideanMapping3 | optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPose (const QVEuclideanMapping3 &camera0, const QList< QPointF > &points2D, const QList< QV3DPointF > &points3D, const int iterations=5) |
| Improves the estimated location of a camera pose by refining its reprojection error. | |
| QV3DPointF | optimizeReprojectionErrorFor3DPoint (const QV3DPointF &initialPoint3D, const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > &cameraPoses, const QHash< int, QPointF > &projectionsOfAPoint, const int iterations=5, const double lambda=1e+0) |
| Improves the estimated location of a 3D point by refining its reprojection error. | |
| QVCameraPose | optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPoseCauchy (const QVCameraPose &cameraPose, const QList< QPointF > &points2D, const QList< QV3DPointF > &points3D, const int iterations, const double lambda=1e-5, const double sigma=3.0) |
| Improves the estimated location of a camera pose by refining its reprojection error robustified by a Cauchy distribution. | |
Functions related to Projective Geometry.
The projective geometry is the study of the geometric properties of physical objects when projected in the image plane. It provides theoretical tools to obtain 3D reconstructions and measurements of real world objects and scenes from the geometry and location of their distinctive features in images.
In this module you can find functions to:
Most of these algorithms are described in the book Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision by R. Hartley and A. Zisserman. The references to this book in this documentation correspond to the second edition.
From fundamental and essential matrices.
| bool computeFundamentalMatrix | ( | const QVector< QPointFMatching > & | matchings, | |
| QVMatrix & | F, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | svdMethod = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the fundamental matrix between two images using the 8-point algorithm.
This function obtains the fundamental matrix between two images using the 8-point algorithm. It is faster than the overloaded version.
| matchings | list of 8 or more point matchings. | |
| F | output fundamental matrix. | |
| svdMethod | method used in several SVD internal decompositions of the algorithm. |
Definition at line 208 of file qvepipolar.cpp.
Referenced by getCameraFocals(), and linearCameraPairInitialization().
| double symmetricEpipolarDistance | ( | const QVMatrix & | F, | |
| const QPointFMatching & | matching | |||
| ) |
Evaluate symmetric epipolar error for a fundamental matrix defined between two images and one image point correspondence.
This function returns the epipolar error defined for the image point correspondence with the following expression:
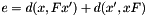
Where 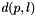 is the euclidean distance in the 2D plane between the point
is the euclidean distance in the 2D plane between the point 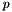 and the line
and the line  .
.
| F | Fundamental matrix. | |
| matching | Image point matching. |
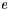 .
. Definition at line 253 of file qvepipolar.cpp.
Referenced by symmetricEpipolarDistance().
| QVVector symmetricEpipolarDistance | ( | const QVMatrix & | F, | |
| const QVector< QPointFMatching > & | matchings | |||
| ) |
Evaluate symmetric epipolar errors for a fundamental matrix defined between two images and a list of image point correspondences.
This function returns a vector containing the symmetric epipolar errors defined for the image point correspondences with the following expression:
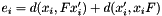
Where 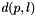 is the euclidean distance in the 2D plane between the point
is the euclidean distance in the 2D plane between the point 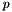 and the line
and the line  .
.
| F | fundamental matrix. | |
| matchings | list of point matchings. |
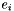 for each matching.
for each matching. Definition at line 302 of file qvepipolar.cpp.
| bool computeProjectiveHomography | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings, | |
| QVMatrix & | H | |||
| ) |
Obtains a planar homography from a list of point correspondences.
This function obtains the homography matrix 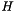 corresponding to the projective transformation which most closely map a set of four or more point correspondences.
corresponding to the projective transformation which most closely map a set of four or more point correspondences.
These projective homographies can be used to obtain a frontal view of any planar figure appearing in an image. The following is an example of planar rectification:

Image on the left is the original picture obtained with a pin-hole camera. Image on the right was obtained mapping the pixels in the original image with the planar homography obtained using the function ComputeProjectiveHomography.
The homography 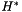 is obtained identifying the four corners of the chessboard, and their corresponding coordinates in the plane of the chessboard:
is obtained identifying the four corners of the chessboard, and their corresponding coordinates in the plane of the chessboard:
QList< QPair<QPointF, QPointF> > matchings; matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(-171,109), QPointF(-100,+100))); matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(-120,31), QPointF(-100,-100))); matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(117,53), QPointF(+100,-100))); matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(11,115), QPointF(+100,+100))); const QVMatrix H = ComputeProjectiveHomography(matchings);
by solving the following inequation:
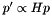
maximizing the average of the algebraic reprojection error for the point matchings 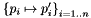 contained in the matchings list:
contained in the matchings list:
![$ H^* = \arg\max \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i=0}^n \left[ p_i' \right] _\times H p_i $](form_157.png)
The points in the original image can be mapped with the homography matrix 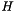 using the ApplyHomography functions.
using the ApplyHomography functions.
| matchings | list of point matchings from the original location, to the destination location. | |
| H | output homography matrix |
Definition at line 131 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by computeProjectiveHomography().
| QVMatrix computeProjectiveHomography | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings | ) |
Obtains a planar homography from a list of point correspondences.
| matchings | list of point matchings from the original location, to the destination location. |
Definition at line 1329 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVMatrix computeAffineHomography | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings | ) |
Obtains an affine homography from a list of point correspondences.
This function obtains the homography matrix 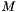 which most closely maps the source points to their destination, in the input point matching list. This homography matrix corresponds to an affine transformation.
which most closely maps the source points to their destination, in the input point matching list. This homography matrix corresponds to an affine transformation.
The function returns the matrix corresponding to the planar homography, from a list of three or more point correspondences between the location of those points at the source plane and their location in the destination plane.
Usage:
QList< QPair<QPointF, QPointF> > matchings; matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(-171,109), QPointF(-100,+100))); matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(-120,31), QPointF(-100,-100))); matchings.append(QPair<QPointF, QPointF>(QPointF(117,53), QPointF(+100,-100))); const QVMatrix M = ComputeAffineHomography(matchings);
Any point 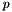 from the 2D plane can be mapped to another point in the plane
from the 2D plane can be mapped to another point in the plane 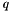 with an affine matrix
with an affine matrix 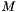 using the following C++ code:
using the following C++ code:
QPointF q = M * QVVector::homogeneousCoordinates(p);
Or by using the ApplyHomography functions.
| matchings | list of point matchings from the original location, to the destination location. |
Definition at line 227 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVMatrix computeSimilarHomography | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings | ) |
Obtains a similar homography from a set of inter-image point matchings.
A similar transformation is obtained by composing an euclidean transformation with a scaling.
This function obtains a similar mapping between the source an destination locations of a set of point matchings. The mapping is returned as a 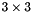 matrix which can be multiplied to the source location of each mapping point in homogeneous coordinates, to obtain the location of the mapped point.
matrix which can be multiplied to the source location of each mapping point in homogeneous coordinates, to obtain the location of the mapped point.
The returned matrix has the following structure:
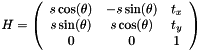
Where 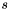 is the scale factor, and
is the scale factor, and 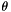 and
and 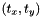 are the rotation angle and translation vector of the euclidean mapping respectively.
are the rotation angle and translation vector of the euclidean mapping respectively.
Definition at line 275 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVMatrix cvFindFundamentalMat | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings | ) |
Obtains the fundamental matrix between two images, using the 8 point algorithm.
This function performs point normalization to robustly obtain the F matrix.
| matchings | list containing at least 8 image point correspondences. |
Definition at line 540 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by cvFindFundamentalMat(), and getCameraFocals().
| QPointF applyHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | homography, | |
| const QPointF & | point | |||
| ) |
Maps a point using an homography.
This function maps a point 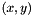 in the 2D plane, using a planar homography. The homography is represented as a
in the 2D plane, using a planar homography. The homography is represented as a 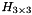 matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography from a set of point correspondences between the original 2D plane, and the mapped plane.
matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography from a set of point correspondences between the original 2D plane, and the mapped plane.
The output of the function is a point 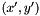 which satisfies the following equation:
which satisfies the following equation:
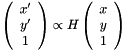
| homography | The homography transformation matrix | |
| point | Point to apply the homography transformation |
Definition at line 646 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by applyHomography(), and correctIntrinsics().
| QList<QPointF> applyHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | homography, | |
| const QList< QPointF > & | sourcePoints | |||
| ) |
Maps a set of points using an homography.
This is an overloaded version of the ApplyHomography(const QVMatrix &, const QPointF &) function provided by convenience. This function takes a list of points from the 2D plane, and an homography matrix as inputs. The output will be a list of points obtained by mapping the points from the input list, using the homography.
| homography | The homography transformation matrix | |
| sourcePoints | Points to apply the homography transformation |
Definition at line 657 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVImage<uChar, 1> applyHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | homography, | |
| const QVImage< uChar, 1 > & | image, | |||
| const int | interpolation = IPPI_INTER_CUBIC | |||
| ) |
Performs an homography distortion on an image.
The homography is represented as a 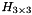 matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography.
matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography.
This function takes a single channel image, and an homography matrix as inputs. Each point 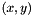 in the input image is mapped to its location in the resulting image
in the input image is mapped to its location in the resulting image 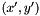 using the homography
using the homography 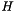 as follows:
as follows:
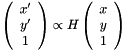
| homography | The homography transformation matrix | |
| image | The input image to distort | |
| interpolation | Type of interpolation. Possible values for this parameter are:
|
Definition at line 666 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVImage<uChar, 3> applyHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | homography, | |
| const QVImage< uChar, 3 > & | image, | |||
| const int | interpolation = IPPI_INTER_CUBIC | |||
| ) |
Performs an homography distortion on an image.
The homography is represented as a 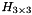 matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography.
matrix. These matrices can be obtained using methods like ComputeSimilarHomography, ComputeProjectiveHomography, or ComputeAffineHomography.
This function takes a three channel image, and an homography matrix as inputs. Each point 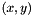 in the input image is mapped to its location in the resulting image
in the input image is mapped to its location in the resulting image 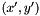 using the homography
using the homography 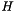 as follows:
as follows:
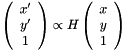
| homography | The homography transformation matrix | |
| image | The input image to distort | |
| interpolation | Type of interpolation. Possible values for this parameter are:
|
Definition at line 673 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| void getCameraPosesFromEssentialMatrix | ( | const QVMatrix & | E, | |
| QVMatrix & | R1, | |||
| QVMatrix & | R2, | |||
| QV3DPointF & | t | |||
| ) |
Decomposes an essential matrix and obtains the corresponding pair of camera poses.
This function obtains the four possible pairs of valid camera poses from an essential matrix:
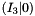 and
and 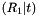
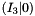 and
and 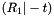
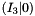 and
and 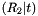
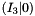 and
and 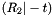
These camera poses satisfy the following equation:
![$ E \propto \left[ t \right] _\times R_i $](form_171.png)
This function returns the two rotation matrices (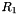 and
and 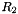 ) and the vector
) and the vector 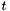 from those expressions.
from those expressions.
See section 9.6.2 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision for more info on decomposing the essential matrix to obtain the camera poses.
| E | The input essential matrix. | |
| R1 | Output param containing the first possible rotation matrix. | |
| R2 | Output param containing the second possible rotation matrix. | |
| t | Output param containing the translation vector. |
Definition at line 1219 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by linearCameraPairInitialization().
| bool testCheiralityForCameraPoses | ( | const QVMatrix & | sourceRt, | |
| const QPointF & | sourceProjection, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | destRt, | |||
| const QPointF & | destProjection | |||
| ) |
Tests if two camera poses satisfy the cheirality condition for the reconstruction of a 3D point.
This function reconstructs a 3D point from its projections on two image views, and test whether the triangulated location is in front or behind of the cameras. If the point is not in front of both cameras, the 3D reconstruction obtained from these camera poses will be incorrect.
See chapter 20 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision for more info on cheirality.
| sourceRt | Camera pose for the first view. | |
| sourceProjection | Projection of the point used to test cheirality on the first view. | |
| destRt | Camera pose for the second view. | |
| destProjection | Projection of the point used to test cheirality on the second view. |
Definition at line 1241 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by linearCameraPairInitialization(), and testCheirality().
| QVMatrix linearCameraResection | ( | const QList< QPointF > & | points2d, | |
| const QList< QV3DPointF > & | points3d | |||
| ) |
Obtains the camera matrix from a set of correspondences between 3D points and their respective image projections.
The following formula models the relation between a set of points from the 3D world 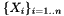 and their projections
and their projections 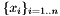 on an image:
on an image:
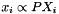
This function uses a direct linear transformation (DLT) to obtain the camera matrix 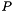 from a given set of 3D points and their corresponding image points.
from a given set of 3D points and their corresponding image points.
For more information about the linear camera resection, check chapter 7 of 'Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision', section 7.1.
| points2d | List containing the points from the image. | |
| points3d | List containing the 3D points. |
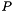 .
. Definition at line 896 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QV3DPointF linear3DPointTriangulation | ( | const QVector< QVMatrix > & | cameraMatrices, | |
| const QHash< int, QPointF > & | projectionsOfAPoint, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on several views, and their corresponding camera matrices.
This is an overloaded version of the function linear3DPointTriangulation(const QList<QVMatrix> &, const QList<QPointF> &), provided for convenience.
This version does not require that the point were visible from every camera in the input camera list. The point projections are provided in a QHash structure. Each key in that structure is the index at the camera list of the camera corresponding to the point projection.
Definition at line 1011 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QV3DPointF linear3DPointTriangulation | ( | const QList< QVMatrix > & | cameraMatrices, | |
| const QList< QPointF > & | projectionsOfAPoint, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on several views, and their corresponding camera matrices.
Using the projection formula:
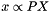
This function triangulates the location of the 3D point 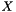 , provided the projections
, provided the projections 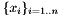 on several views, and the camera matrices
on several views, and the camera matrices 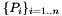 for those views.
for those views.
The method used is described at section 12.2 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision.
| cameraMatrices | list of camera matrices for the different views. | |
| projectionsOfAPoint | list of projections of the 3D point for the different views. |
Definition at line 969 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by linear3DPointsTriangulation(), linear3DPointTriangulation(), and testCheiralityForCameraPoses().
| QV3DPointF linear3DPointTriangulation | ( | const QPointF & | point1, | |
| const QVMatrix & | P1, | |||
| const QPointF & | point2, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | P2, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices.
Using the projection formula:
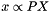
This function triangulates the location of the 3D point 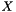 , provided the projections
, provided the projections 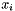 and
and 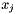 on two views, and the camera matrices
on two views, and the camera matrices 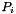 and
and 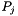 for those views.
for those views.
The method used is described at section 12.2 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision.
| point1 | The projected location of the 3D point in the first image. | |
| P1 | The camera matrix for the first image. | |
| point2 | The projected location of the 3D point in the second image. | |
| P2 | The camera matrix for the second image. |
Definition at line 1337 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QV3DPointF linear3DPointTriangulation | ( | const QPointFMatching & | matching, | |
| const QVMatrix & | P1, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | P2, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices.
Using the projection formula:
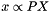
This function triangulates the location of the 3D point 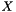 , provided the point matchings
, provided the point matchings 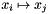 between two views, and the camera matrices
between two views, and the camera matrices 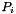 and
and 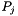 for those views.
for those views.
The method used is described at section 12.2 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision.
| matching | Point matching containing the projections of each 3D point at both cameras. | |
| P1 | The camera matrix for the first image. | |
| P2 | The camera matrix for the second image. | |
| method | The method to solve the linear system. |
Definition at line 1050 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QV3DPointF linear3DPointTriangulation | ( | const QPointFMatching & | matching, | |
| const QVCameraPose & | pose1, | |||
| const QVCameraPose & | pose2, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of a 3D point from its projection on two images, and their corresponding camera matrices.
Using the projection formula:
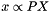
This function triangulates the location of the 3D point 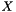 , provided the point matchings
, provided the point matchings 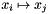 between two views, and the camera matrices
between two views, and the camera matrices 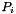 and
and 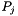 for those views.
for those views.
The method used is described at section 12.2 from Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision.
| matching | Point matching containing the projections of each 3D point at both cameras. | |
| pose1 | The camera pose for the first image. | |
| pose2 | The camera pose for the second image. | |
| method | The method to solve the linear system. |
Definition at line 1088 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QList<QV3DPointF> linear3DPointsTriangulation | ( | const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > & | cameras, | |
| const QList< QHash< int, QPointF > > & | pointProjections, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices.
Using function linear3DPointTriangulation, the locations of several 3D points are triangulated with this function.
| cameras | List of cameras. | |
| pointProjections | Container for the point projections. Each element in this list corresponds to a 3D point. These elements are hash tables, containing the point image projections, indexed by the number of the camera. |
Definition at line 1111 of file qvprojective.cpp.
Referenced by reconstructionError().
| QList<QV3DPointF> linear3DPointsTriangulation | ( | const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > & | cameras, | |
| const QVector< QHash< int, QPointF > > & | pointProjections, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices.
This is an overloaded version of the previous function.
| cameras | List of cameras. | |
| pointProjections | Container for the point projections. Each element in this list corresponds to a 3D point. These elements are hash tables, containing the point image projections, indexed by the number of the camera. |
Definition at line 1127 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QList<QV3DPointF> linear3DPointsTriangulation | ( | const QList< QVCameraPose > & | cameras, | |
| const QList< QHash< int, QPointF > > & | pointProjections, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices.
Using function linear3DPointTriangulation, the locations of several 3D points are triangulated with this function.
| cameras | List of cameras. | |
| pointProjections | Container for the point projections. Each element in this list corresponds to a 3D point. These elements are hash tables, containing the point image projections, indexed by the number of the camera. |
Definition at line 1143 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QList<QV3DPointF> linear3DPointsTriangulation | ( | const QList< QVCameraPose > & | cameras, | |
| const QVector< QHash< int, QPointF > > & | pointProjections, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Recovers the location of several 3D points from their projections on different views, and the corresponding camera matrices.
This is an overloaded version of the previous function.
| cameras | List of cameras. | |
| pointProjections | Container for the point projections. Each element in this list corresponds to a 3D point. These elements are hash tables, containing the point image projections, indexed by the number of the camera. |
Definition at line 1159 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| bool getCameraFocals | ( | const QList< QPointFMatching > & | matchings, | |
| double & | focal1, | |||
| double & | focal2, | |||
| const QPointF | principalPoint1 = QPointF(0.0, 0.0), |
|||
| const QPointF | principalPoint2 = QPointF(0.0, 0.0), |
|||
| const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType | gslMinimizerAlgorithm = VectorBFGS, |
|||
| const int | optimizationIterations = 50 | |||
| ) |
Estimates the focal lengths for two cameras,.
This function can be used to calibrate two cameras, provided a rough approximation of their principal point locations, and a list of point correspondences between two images.
It first obtains two initial estimations for the focal lengths 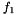 and
and 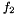 of the cameras using the procedure described in [1]. These focal distances are refined by optimizing the following calibration error function:
of the cameras using the procedure described in [1]. These focal distances are refined by optimizing the following calibration error function:
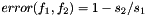
where the values 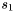 and
and 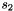 correspond to the first and second singular values of the following matrix:
correspond to the first and second singular values of the following matrix:
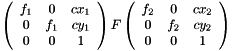
where 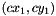 and
and 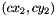 are the provided rough approximations for the principal points of the first and second camera respectively, and
are the provided rough approximations for the principal points of the first and second camera respectively, and 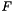 is the fundamental matrix obtained from the list of point correspondences.
is the fundamental matrix obtained from the list of point correspondences.
[1] Estimation of Relative Camera Positions for Uncalibrated Cameras. R. Hartley. Proceedings of the Second European Conference on Computer Vision, 1992.
| matchings | List of point matchings between the two images. | |
| focal1 | This variable will contain the focal for the first camera in return. | |
| focal2 | This variable will contain the focal for the second camera in return. | |
| principalPoint1 | Rough approximation for the principal point of the first camera. | |
| principalPoint2 | Rough approximation for the principal point of the second camera. | |
| gslMinimizerAlgorithm | Algorithm to use in the optimization step of the focal calibration. | |
| optimizationIterations | Number of iterations to perform at the optimization step. |
Definition at line 512 of file getCameraFocals.cpp.
| double computeCameraFocalFromPlanarHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | H, | |
| int | w, | |||
| int | h, | |||
| bool | byzero = false | |||
| ) |
Compute camera focal from a planar homography.
This function computes the camera focal by solving for diagonal matrix IAC 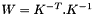 , taking into account that
, taking into account that 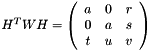
This is equivalent to two different constraints in the entries of H, one of them to force
(1) 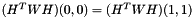
and the other to force
(2) 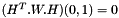
If we want to use the first condition, we set byzero to false; if we want to use de second, we set byzero to true. (Of course, we could have also used both conditions at the same time, and solve by minimum squares).
| H | planar homography matrix | |
| w | horizontal coordinate for the principal point of the image | |
| h | vertical coordinate for the principal point of the image | |
| byzero | If true, use equation (1) to solve for the focal value. Otherwise, use equation (2) |
Definition at line 1283 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVCameraPose getCameraPoseFromCalibratedHomography | ( | const QVMatrix & | K, | |
| const QVMatrix & | H | |||
| ) |
Estimates the camera pose form the intrinsic calibration and a planar homography.
| K | Intrinsic calibration matrix for the camera. | |
| H | Planar homography. |
Definition at line 1292 of file qvprojective.cpp.
| QVEuclideanMapping3 optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPose | ( | const QVEuclideanMapping3 & | camera0, | |
| const QList< QPointF > & | points2D, | |||
| const QList< QV3DPointF > & | points3D, | |||
| const int | iterations = 5 | |||
| ) |
Improves the estimated location of a camera pose by refining its reprojection error.
Provided a set of 3D points and their estimated projections on an image, this function improves the pose for that view, by refining the 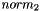 of the reprojection error using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization.
of the reprojection error using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization.
| cameraPose | Initial camera pose. | |
| points2D | List of image projections for the points | |
| points3D | List of 3D coordinates for the points | |
| iterations | Number of Levenberg-Marquard iterations to perform |
Definition at line 154 of file qvreprojectionerror.cpp.
| QV3DPointF optimizeReprojectionErrorFor3DPoint | ( | const QV3DPointF & | initialPoint3D, | |
| const QList< QVEuclideanMapping3 > & | cameraPoses, | |||
| const QHash< int, QPointF > & | projectionsOfAPoint, | |||
| const int | iterations = 5, |
|||
| const double | lambda = 1e+0 | |||
| ) |
Improves the estimated location of a 3D point by refining its reprojection error.
Provided the estimated projections of a 3D point on a set of views, and the estimated camera poses for those views, this function improves the estimated location of the 3D point by refining the 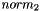 of the reprojection error using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization.
of the reprojection error using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization.
| initialPoint3D | Initial 3D point location. | |
| cameraPoses | List of the views camera poses. | |
| projectionsOfAPoint | List of projections of the 3D point on the views. | |
| iterations | Number of iterations to refine reprojection error. | |
| lambda | Value to increase the diagonal of the Hessian matrix in the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. |
Definition at line 267 of file qvreprojectionerror.cpp.
| QVCameraPose optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPoseCauchy | ( | const QVCameraPose & | cameraPose, | |
| const QList< QPointF > & | points2D, | |||
| const QList< QV3DPointF > & | points3D, | |||
| const int | iterations, | |||
| const double | lambda = 1e-5, |
|||
| const double | sigma = 3.0 | |||
| ) |
Improves the estimated location of a camera pose by refining its reprojection error robustified by a Cauchy distribution.
This function optimizes the pose of a view using the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization, provided the image projections of a set of 3D points.
This method assumes a Cauchy distribution for the reprojection residuals, to reduce the impact of outliers in the cost error, and improve the obtained camera pose.
| cameraPose | Initial camera pose. | |
| points2D | List of image projections for the points | |
| points3D | List of 3D coordinates for the points | |
| iterations | Number of Levenberg-Marquard iterations to perform | |
| lambda | Increment of the diagonal elements for the estimated Hessian matrix | |
| sigma | standard deviation to the cost function (negative log-likelihood) |
Definition at line 455 of file qvreprojectionerror.cpp.