 PARP Research Group
PARP Research Group
 PARP Research Group PARP Research Group |
Universidad de Murcia  |
Numerical analisis and function minimization
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Classes | |
| class | QVFunction< Input, Output > |
| Base class for function objects. More... | |
| class | QVJacobian |
| Class to create jacobian functions. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | GSLMinFMinimizer { GoldenSection = 0, BrentMinimization = 1 } |
GSL Minimization algorithms. More... | |
| enum | GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType { ConjugateFR = 0, ConjugatePR = 1, VectorBFGS = 2, SteepestDescent = 3 } |
GSL multidimensional minimization algorithms using gradient information. More... | |
| enum | GSLMultiminFDFSolverType { LMScaledDerivative = 0, LMDerivative = 1 } |
GSL multidimensional solving. More... | |
Functions | |
| const QVVector | qvEstimateGradient (QVFunction< QVVector, double > &function, const QVVector &point, const double h=1e-6) |
| Estimates the gradient vector for the function using the forward two-points rule for the derivative approximation. | |
| const QVMatrix | qvEstimateJacobian (QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > &function, const QVVector &point, const double h=1e-6) |
| Estimates the Jacobian matrix for the function using the forward two-points rule for the derivative approximation. | |
| const QVMatrix | qvEstimateHessian (QVFunction< QVVector, double > &function, const QVVector &point, const double h=1e-3) |
| Estimates the hessian matrix for the function using the forward two-point rule for the derivative approximation. | |
| bool | qvGSLMinimizeFDF (const QVFunction< QVVector, double > &function, QVVector &point, const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType gslMinimizerAlgorithm=ConjugateFR, const int maxIterations=100, const double maxGradientNorm=1e-3, const double step=0.01, const double tol=1e-4) |
| Wrapper to GSL multivariate function minimization using gradient information. | |
| bool | qvGSLMinimizeFDF (const QVFunction< QVVector, double > &function, const QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > &gradientFunction, QVVector &point, const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType gslMinimizerAlgorithm=ConjugateFR, const int maxIterations=100, const double maxGradientNorm=1e-3, const double step=0.01, const double tol=1e-4) |
| Wrapper to GSL multivariate function minimization using gradient information. | |
| bool | qvGSLSolveFDF (const QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > &function, const QVFunction< QVVector, QVMatrix > &functionJacobian, QVVector &x, const GSLMultiminFDFSolverType gslSolverAlgorithm=LMScaledDerivative, const int maxIterations=100, const double maxAbsErr=1e-4, const double maxRelErr=1e-4) |
| Solves a non-linear system of equations. | |
| bool | qvGSLMinimize (const QVFunction< double, double > &function, double &x, double &lower, double &upper, const GSLMinFMinimizer gslMinimizerAlgorithm=BrentMinimization, const int maxIterations=100, const double absoluteError=1e-3, const double relativeError=0.0) |
| Wrapper to GSL function minimization. | |
Function optimization and numerical derivative evaluation.
| enum GSLMinFMinimizer |
GSL Minimization algorithms.
Definition at line 93 of file qvnumericalanalysis.h.
GSL multidimensional minimization algorithms using gradient information.
Definition at line 108 of file qvnumericalanalysis.h.
GSL multidimensional solving.
| LMScaledDerivative |
Scaled Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. |
| LMDerivative |
Non-scaled (faster) Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. |
Definition at line 127 of file qvnumericalanalysis.h.
| const QVVector qvEstimateGradient | ( | QVFunction< QVVector, double > & | function, | |
| const QVVector & | point, | |||
| const double | h = 1e-6 | |||
| ) |
Estimates the gradient vector for the function using the forward two-points rule for the derivative approximation.
This function obtains a numerical approximation of the gradient at a given point for a function. The forward derivative formula is used to estimate each partial derivative value, component of the gradient vector:
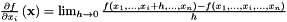
The function to estimate the gradient is provided as a QVFunction object.
| function | object containing the function to estimate gradient. | |
| point | Point to evaluate the gradient vector. | |
| h | Increment coeficient for the derivative formula. |
Definition at line 28 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.
Referenced by qvEstimateHessian().
| const QVMatrix qvEstimateJacobian | ( | QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > & | function, | |
| const QVVector & | point, | |||
| const double | h = 1e-6 | |||
| ) |
Estimates the Jacobian matrix for the function using the forward two-points rule for the derivative approximation.
This function obtains a numerical approximation of the Jacobian of a 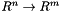 function at a given point. The forward derivative formula is used to estimate each partial derivative value, component of the Jacobian:
function at a given point. The forward derivative formula is used to estimate each partial derivative value, component of the Jacobian:
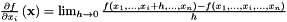
The function to estimate the gradient is provided as a QVFunction object.
| function | function object to estimate Jacobian. | |
| point | Point to evaluate the Jacobian matrix. | |
| h | Increment coeficient for the derivative formula. |
Definition at line 42 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.
| const QVMatrix qvEstimateHessian | ( | QVFunction< QVVector, double > & | function, | |
| const QVVector & | point, | |||
| const double | h = 1e-3 | |||
| ) |
Estimates the hessian matrix for the function using the forward two-point rule for the derivative approximation.
This function obtains a numerical approximation of the hessian matrix at a given pointfor a function. The following formula is used to compute the components fo the hessian matrix:
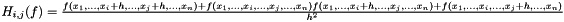
It is derived from the forward derivative formula used to estimate each partial derivative value:
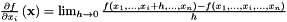
The function to estimate the hessian is provided as a QVFunction object.
| function | object containing the function to estimate hessian. | |
| point | Point to evaluate the hessian matrix. | |
| h | Increment coeficient for the derivative formula. |
Definition at line 58 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.
| bool qvGSLMinimizeFDF | ( | const QVFunction< QVVector, double > & | function, | |
| QVVector & | point, | |||
| const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType | gslMinimizerAlgorithm = ConjugateFR, |
|||
| const int | maxIterations = 100, |
|||
| const double | maxGradientNorm = 1e-3, |
|||
| const double | step = 0.01, |
|||
| const double | tol = 1e-4 | |||
| ) |
Wrapper to GSL multivariate function minimization using gradient information.
This function minimizes a multivariate function contained in a QVFunction object, using the GSL functionality for that purpose. The gradient of that function is estimated using the qvEstimateGradient function, and is used in the minimization process.
An usage example follows:
#include <qvnumericalanalysis.h> // Creation of a quadratic function class type class QuadraticFunction: public QVFunction<QVVector, double> { private: const QVMatrix A; const QVVector b; const double c; double evaluate(const QVVector &x) { return x*A*x + b*x + c; } public: QuadraticFunction(const QVMatrix &A, const QVVector &b, const double c): QVFunction<QVVector, double>(), A(A), b(b), c(c) { } }; // Main code int main() { // Example quadratic function object creation QVMatrix A = QVMatrix::zeros(3,3); QVVector b = QVVector(3,0); double c; A(0,0) = 70; A(1,1) = 11; A(2,2) = 130; b = QVVector(3); b[0] = -100; b[1] = 20; b[2] = -30; c = 100; QuadraticFunction f(A, b, c); // Function minimization QVVector minimum(3,0); qvGSLMinimizeFDF(f, minimum); std::cout << "Function minimum value = " << f(minimum) << std::endl; std::cout << "Reached at point = " << minimum << std::endl;; }
| function | Object containing the function to minimize. | |
| point | Starting point for the minimization. This vector will contain the obtained minimum when the function returns. | |
| gslMinimizerAlgorithm | Minimization algorithm. See enumeration GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType for possible values. | |
| maxIterations | Maximum number of steps to perform by the minimization. | |
| maxGradientNorm | Minimal value of the gradient size (norm 2) to stop the minimization when reached. | |
| step | Corresponds to parameter step for the gsl_multimin_fdfminimizer_set function. | |
| tol | Corresponds to parameter tol for the gsl_multimin_fdfminimizer_set function. |
Definition at line 100 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.
Referenced by getCameraFocals().
| bool qvGSLMinimizeFDF | ( | const QVFunction< QVVector, double > & | function, | |
| const QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > & | gradientFunction, | |||
| QVVector & | point, | |||
| const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType | gslMinimizerAlgorithm = ConjugateFR, |
|||
| const int | maxIterations = 100, |
|||
| const double | maxGradientNorm = 1e-3, |
|||
| const double | step = 0.01, |
|||
| const double | tol = 1e-4 | |||
| ) |
Wrapper to GSL multivariate function minimization using gradient information.
This is an overloaded version of the function qvGSLMinimizeFDF(QVFunction<QVVector, double> &, QVVector &, const GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType, const int, const double, const double, const double) provided for convenience.
The real gradient of the function is used in the form of a vector function object, instead of the numerical approximation qvEstimateGradient to the gradient, which is less accurate and generally less efficient. An example code usage follows:
#include <qvnumericalanalysis.h> // Creation of a quadratic function class type class QuadraticFunction: public QVFunction<QVVector, double> { private: const QVMatrix A; const QVVector b; const double c; double evaluate(const QVVector &x) { return x*A*x + b*x + c; } public: QuadraticFunction(const QVMatrix &A, const QVVector &b, const double c): QVFunction<QVVector, double>(), A(A), b(b), c(c) { } }; // Creation of a quadratic vector function class type, corresponding to the gradient of the previous function class QuadraticFunctionGradient: public QVFunction<QVVector, QVVector> { private: const QVMatrix A; const QVVector b; const double c; QVVector evaluate(const QVVector &x) { return A*x*2 + b; } public: QuadraticFunctionGradient(const QVMatrix &A, const QVVector &b, const double c): QVFunction<QVVector, QVVector>(), A(A), b(b), c(c) { } }; // Main code int main() { // Example quadratic function and corresponding gradient objects creation QVMatrix A = QVMatrix::zeros(3,3); QVVector b = QVVector(3,0); double c; A(0,0) = 70; A(1,1) = 11; A(2,2) = 130; b = QVVector(3); b[0] = -100; b[1] = 20; b[2] = -30; c = 100; QuadraticFunction f(A, b, c); QuadraticFunctionGradient g(A, b, c); // Function minimization QVVector minimum(3,0); qvGSLMinimizeFDF(f, g, minimum); std::cout << "Function minimum value = " << f(minimum) << std::endl; std::cout << "Reached at point = " << minimum << std::endl; }
| function | Object containing the function to minimize. | |
| gradientFunction | Object containing the gradient vector function. | |
| point | Starting point for the minimization. This vector will contain the obtained minimum when the function returns. | |
| gslMinimizerAlgorithm | Minimization algorithm. See enumeration GSLMultiminFDFMinimizerType for possible values. | |
| maxIterations | Maximum number of steps to perform the minimization. | |
| maxGradientNorm | Minimal value of the gradient size (norm 2) to stop the minimization when reached. | |
| step | Corresponds to parameter step for the gsl_multimin_fdfminimizer_set function. | |
| tol | Corresponds to parameter tol for the gsl_multimin_fdfminimizer_set function. |
Definition at line 167 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.
| bool qvGSLSolveFDF | ( | const QVFunction< QVVector, QVVector > & | function, | |
| const QVFunction< QVVector, QVMatrix > & | functionJacobian, | |||
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const GSLMultiminFDFSolverType | gslSolverAlgorithm = LMScaledDerivative, |
|||
| const int | maxIterations = 100, |
|||
| const double | maxAbsErr = 1e-4, |
|||
| const double | maxRelErr = 1e-4 | |||
| ) |
Solves a non-linear system of equations.
This function uses a nonlinear least-squares optimization procedure to obtain a solution for a system of equations. The input of this functions is a function object, containing a 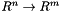 function, that maps the input variables for the system, to the vector of residual values of the system of equations.
function, that maps the input variables for the system, to the vector of residual values of the system of equations.
The function uses the Levenberg-Marquardt optimization algoritm to find an aproximation to a valid solution, starting from an initial guess of the solution.
The optimization finishes when performing a fixed number of maximum iterations. Also, a stopping criteria is applied. The convergence is tested by comparing the last step dx with the absolute error maxAbsErr and relative error maxRelErr to the current position x. The test is true if the following condition is achieved:
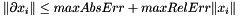
In that case the function stops and returns the point where the function returns the minimum value.
The following code is an usage example of this function. It fits an exponential model on some input measurements:
#include <qvnumericalanalysis.h> class FittingErrorFunction: public QVFunction<QVVector, QVVector> { private: const QVVector x, y; QVVector evaluate(const QVVector &v) { // Evaluate the function QVVector result(y.size(), 0.0); for (int i = 0; i < y.size(); i++) result[i] = v[0] * exp (-v[1] * double(x[i])) + v[2]; // Return residuals return result - y; } public: FittingErrorFunction(const QVVector &x, const QVVector &y): QVFunction<QVVector, QVVector>(), x(x), y(y) { } }; class FittingErrorFunctionJacobian: public QVFunction<QVVector, QVMatrix> { private: const QVVector x, y; QVMatrix evaluate(const QVVector &v) { FittingErrorFunction error(x, y); return qvEstimateJacobian(error, v); } public: FittingErrorFunctionJacobian(const QVVector &x, const QVVector &y): QVFunction<QVVector, QVMatrix>(), x(x), y(y) { } }; int main() { QVVector x, y; for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) { x << double(i); y << 1.0 + 5 * exp (-0.1 * double(i)); } // Create initial guess, and objective functions. QVVector v(3, 0.0); FittingErrorFunction function(x, y); FittingErrorFunctionJacobian functionJacobian(x, y); qvGSLSolveFDF (function, functionJacobian, v, LMScaledDerivative, 500); std::cout << "Solution for the system obtained at " << v << std::endl; }
| function | Function representing the residuals of the system of equations. | |
| functionJacobian | Jacobian of the residual function. | |
| x | Initial guess of the solution. Also, the minimum value will be stored in this variable. | |
| gslSolverAlgorithm | The algorithm to perform minimization. | |
| maxIterations | Maximum number of iterations to perform optimization. | |
| maxAbsErr | Maximal absolute error in the optimization stop condition. | |
| maxRelErr | Maximal relative error in the optimization stop condition. |
| bool qvGSLMinimize | ( | const QVFunction< double, double > & | function, | |
| double & | x, | |||
| double & | lower, | |||
| double & | upper, | |||
| const GSLMinFMinimizer | gslMinimizerAlgorithm = BrentMinimization, |
|||
| const int | maxIterations = 100, |
|||
| const double | absoluteError = 1e-3, |
|||
| const double | relativeError = 0.0 | |||
| ) |
Wrapper to GSL function minimization.
This function uses the GSL to obtain the minimum of a function, provided in a QVFunction object. An example code usage follows:
#include <qvnumericalanalysis.h> // Creation of a sinoidal function class type class SinoidalFunction: public QVFunction<double, double> { private: double evaluate(const double &x) const { return cos(x) + 1.0; } public: SinoidalFunction(): QVFunction<double, double>() { }; }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { const SinoidalFunction function; double x = 2.0, lower = 0.0, upper = 6.0; qvGSLMinimize(function, x, lower, upper); printf ("Minimum found at %.7f\n", x); exit(0); }
| function | Object containing the function to minimize. | |
| x | Starting value for the minimization. This variable will contain the obtained minimum when the function returns. | |
| gslMinimizerAlgorithm | Minimization algorithm. See enumeration GSLMinFMinimizer for possible values. | |
| lower | Minimal value for the search range. | |
| upper | Maximum value for the search range. | |
| maxIterations | Maximum number of steps to perform the minimization. | |
| maxGradientNorm | Minimal value of the gradient size (norm 2) to stop the minimization when reached. | |
| absoluteError | Corresponds to parameter epsabs for the gsl_min_test_interval function. | |
| relativeError | Corresponds to parameter epsrel for the gsl_min_test_interval function. |
Definition at line 302 of file qvnumericalanalysis.cpp.