 PARP Research Group
PARP Research Group
 PARP Research Group PARP Research Group |
Universidad de Murcia  |
Matrix Algebra
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enumerations | |
| enum | TQVSVD_Method { GSL_THIN_DECOMP_MOD, GSL_THIN_DECOMP, GSL_THIN_DECOMP_JACOBI, LAPACK_FULL_DGESVD, LAPACK_FULL_DGESDD, LAPACK_THIN_DGESVD, LAPACK_THIN_DGESDD } |
Available methods for Singular Value Decomposition (SVD). More... | |
| enum | TQVSV_Method { GSL_ONLY_DECOMP_MOD, GSL_ONLY_DECOMP, GSL_ONLY_DECOMP_JACOBI, LAPACK_ONLY_DGESVD, LAPACK_ONLY_DGESDD } |
Available methods for Singular Values only computation (SV). More... | |
| enum | TQVCholesky_Method { GSL_CHOLESKY, LAPACK_CHOLESKY_DPOTRF } |
Available methods for Cholesky Decomposition. More... | |
| enum | TQVQR_Method { GSL_HOUSEHOLDER_THIN_QR, GSL_HOUSEHOLDER_FULL_QR, LAPACK_THIN_DGEQR2, LAPACK_FULL_DGEQR2 } |
Available methods for QR Decomposition. More... | |
| enum | TQVLU_Method { GSL_LU, LAPACK_DGETRF } |
Available methods for LU Decomposition. More... | |
| enum | TQVEigenDecomposition_Method { GSL_EIGENSYMM, LAPACK_DSYEV } |
Available methods for EigenDecomposition. More... | |
| enum | TQVEigenValues_Method { GSL_EIGENSYMM_ONLY, LAPACK_DSYEV_ONLY } |
Available methods for EigenValues only computation. More... | |
| enum | TQVSparseSolve_Method { QVMKL_DSS = 0, QVMKL_ISS = 1, QVCHOLMOD_DSS = 2, QV_SCG = 3, QV_BJPCG = 4, QV_DENSE = 5 } |
Available methods for sparse linear system solving. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | singularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &U, QVVector &s, QVMatrix &V, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
Obtains the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a rectangular  matrix M. matrix M. | |
| void | solveFromSingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &U, const QVVector &s, const QVMatrix &V, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition 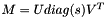 . . | |
| void | solveFromSingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &U, const QVVector &s, const QVMatrix &V, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition 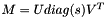 . . | |
| void | solveBySingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the singular value decomposition , using the singular value decomposition 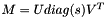 . . | |
| void | solveBySingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the singular value decomposition , using the singular value decomposition 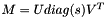 . . | |
| void | solveBySingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, QVMatrix &U, QVVector &s, QVMatrix &V, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the singular value decomposition , using the singular value decomposition 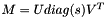 . . | |
| void | solveBySingularValueDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, QVMatrix &U, QVVector &s, QVMatrix &V, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the singular value decomposition , using the singular value decomposition 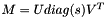 . . | |
| double | singularValueDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &U, const QVVector &s, const QVMatrix &V) |
| Checks for correctness of the SVD of a matrix. | |
| void | singularValues (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &s, const TQVSV_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSV_METHOD) |
| Gets the singular values of a matrix. | |
| double | singularValuesResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVVector &s) |
| Checks for correctness of the singular values of a matrix. | |
| void | CholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &L, const TQVCholesky_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD) |
| Obtains the Cholesky decomposition of a symmetric and positive definite matrix. | |
| void | solveFromCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &L, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition 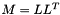 . . | |
| void | solveFromCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &L, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition 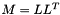 . . | |
| void | solveByCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, const TQVCholesky_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the Cholesky decomposition , using the Cholesky decomposition 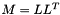 . . | |
| void | solveByCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, const TQVCholesky_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the Cholesky decomposition , using the Cholesky decomposition 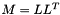 . . | |
| void | solveByCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, QVMatrix &L, const TQVCholesky_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the Cholesky decomposition , using the Cholesky decomposition 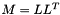 . . | |
| void | solveByCholeskyDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, QVMatrix &L, const TQVCholesky_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the Cholesky decomposition , using the Cholesky decomposition 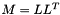 . . | |
| double | CholeskyDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &L) |
| Checks for correctness of the Cholesky decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | LUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &P, QVMatrix &L, QVMatrix &U, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
Obtains the LU decomposition of a rectangular  matrix. matrix. | |
| void | solveFromLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &P, const QVMatrix &L, const QVMatrix &U, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained LU decomposition of M: , using the previously obtained LU decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveFromLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &P, const QVMatrix &L, const QVMatrix &U, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained LU decomposition , using the previously obtained LU decomposition 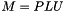 . . | |
| void | solveByLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the LU decomposition , using the LU decomposition 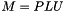 . . | |
| void | solveByLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the LU decomposition , using the LU decomposition 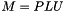 . . | |
| void | solveByLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, QVMatrix &P, QVMatrix &L, QVMatrix &U, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the LU decomposition , using the LU decomposition 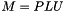 . . | |
| void | solveByLUDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, QVMatrix &P, QVMatrix &L, QVMatrix &U, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the LU decomposition , using the LU decomposition 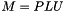 . . | |
| double | LUDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &P, const QVMatrix &L, const QVMatrix &U) |
| Checks for correctness of the LU decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | QRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &Q, QVMatrix &R, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Obtains the QR decomposition of a rectangular  matrix. matrix. | |
| double | QRDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &Q, const QVMatrix &R) |
| Checks for correctness of the QR decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | QLDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &Q, QVMatrix &L, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Obtains the QL decomposition of a rectangular  matrix. matrix. | |
| double | QLDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &Q, const QVMatrix &L) |
| Checks for correctness of the QL decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | RQDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &R, QVMatrix &Q, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Obtains the RQ decomposition of a rectangular  matrix. matrix. | |
| double | RQDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &R, const QVMatrix &Q) |
| Checks for correctness of the RQ decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | LQDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &L, QVMatrix &Q, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Obtains the LQ decomposition of a rectangular  matrix. matrix. | |
| double | LQDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &L, const QVMatrix &Q) |
| Checks for correctness of the LQ decomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | solveFromQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &Q, const QVMatrix &R, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M: , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveFromQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &Q, const QVMatrix &R, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M: , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveByQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the QR decomposition of M: , using the QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveByQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the QR decomposition of M: , using the QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveByQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B, QVMatrix &Q, QVMatrix &R, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix for the unknown matrix  , using the QR decomposition of M: , using the QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | solveByQRDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, QVMatrix &Q, QVMatrix &R, const TQVQR_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector for the unknown vector  , using the QR decomposition of M: , using the QR decomposition of M: | |
| void | eigenDecomposition (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &lambda, QVMatrix &Q, const TQVEigenDecomposition_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVEIGENDECOMPOSITION_METHOD) |
| Obtains the eigen-decomposition of a symmetric matrix. | |
| double | eigenDecompositionResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVVector &lambda, const QVMatrix &Q) |
| Checks for correctness of the eigendecomposition of a matrix. | |
| void | eigenValues (const QVMatrix &M, QVVector &lambda, const TQVEigenValues_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVEIGENVALUES_METHOD) |
| Gets the eigenvalues of a matrix. | |
| double | eigenValuesResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVVector &lambda) |
| Checks for correctness of the eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix. | |
| QVMatrix | pseudoInverse (const QVMatrix &M, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD, const double epsilon=1.0E-10) |
| Obtains the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse of a matrix. | |
| double | determinant (const QVMatrix &M, const TQVLU_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD) |
| Obtains the determinant of a square matrix. | |
| void | solveHomogeneous (const QVMatrix &A, QVector< double > &x, const TQVSVD_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD) |
| Solves an homogeneous linear system of equations. | |
| double | solveResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVMatrix &X, const QVMatrix &B) |
| Returns the residual of the solution to a linear matrix equation. | |
| double | solveResidual (const QVMatrix &M, const QVVector &x, const QVVector &b) |
| Returns the residual of the solution to a linear vector equation. | |
| double | sparseSolve (const QVSparseBlockMatrix &M, QVVector &x, const QVVector &b, const bool isSymmetric=false, const bool isPosDefinite=false, const TQVSparseSolve_Method method=DEFAULT_TQVSPARSESOLVE_METHOD, const bool start_from_x=false, const bool iters_or_resid=true, const int iters=0, const double resid=1.0E-10, int &final_iter_count=dummy) |
| Solves a sparse system of linear equations, taking advantage of sparseness to accelerate the computation. | |
| bool | solveHomogeneous (const QVSparseBlockMatrix &A, QVVector &x, const int maxIterations=10, const double minRelativeError=0.0, const TQVSparseSolve_Method method=QVMKL_DSS) |
| Solves a sparse homogeneous linear system using the inverse iteration algorithm and the MKL sparse routines. | |
Matrix algebra related functions (see also source programs in directory examples/matrixalgebra-tests for an exhaustive set of examples of use).
| enum TQVSVD_Method |
Available methods for Singular Value Decomposition (SVD).
Definition at line 75 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
| enum TQVSV_Method |
Available methods for Singular Values only computation (SV).
Definition at line 87 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
| enum TQVCholesky_Method |
Available methods for Cholesky Decomposition.
Definition at line 97 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
| enum TQVQR_Method |
Available methods for QR Decomposition.
Definition at line 104 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
| enum TQVLU_Method |
Available methods for LU Decomposition.
| GSL_LU |
GSL (Gauss elimination with partial pivoting method); |
| LAPACK_DGETRF |
Lapack DGETRF (Gauss elimination with partial pivoting); |
Definition at line 113 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
Available methods for EigenDecomposition.
| GSL_EIGENSYMM |
GSL eigendecomposition of a real symmetric matrix (eigenvalues and eigenvectors); |
| LAPACK_DSYEV |
Lapack DSYEV eigendecomposition (eigenvalues and eigenvectors); |
Definition at line 120 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
Available methods for EigenValues only computation.
| GSL_EIGENSYMM_ONLY |
GSL eigendecomposition of a real symmetric matrix (eigenvalues only); |
| LAPACK_DSYEV_ONLY |
Lapack DSYEV eigendecomposition (eigenvalues only); |
Definition at line 127 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
Available methods for sparse linear system solving.
Definition at line 134 of file qvmatrixalgebra.h.
| void singularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| QVVector & | s, | |||
| QVMatrix & | V, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a rectangular  matrix M.
matrix M.
The SV decomposition obtains two matrices U and V and a vector s from an original matrix M satisfying the following equation:
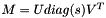
If the decomposition method is 'full', both U and V are square matrices of sizes  and
and  , respectively, while the
, respectively, while the 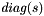 matrix is of size
matrix is of size  , with all values zero, except on values
, with all values zero, except on values 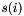 on its main diagonal, which correspond to the singular values in decreasing order.
on its main diagonal, which correspond to the singular values in decreasing order.
If the decomposition is 'thin', then U and V are only of sizes 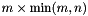 and
and 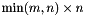 , while the
, while the 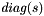 matrix is square of size
matrix is square of size 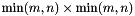 , and containing the singular values in decreasing order in the elements of its diagonal.
, and containing the singular values in decreasing order in the elements of its diagonal.
In any case, both matrices U and V have always orthonormal columns (that is, 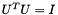 and
and 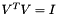 ), and if the decomposition method is 'full', are fully orthogonal square matrices.
), and if the decomposition method is 'full', are fully orthogonal square matrices.
| M | input matrix to decompose | |
| U | param to store the matrix U from the SVD decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| s | param to store the s vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| V | param to store the matrix V from the SVD decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVSVD_Method) |
Definition at line 204 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by computeProjectiveHomography(), getCameraPosesFromEssentialMatrix(), pseudoInverse(), and solveHomogeneous().
| void solveFromSingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | U, | |
| const QVVector & | s, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | V, | |||
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition
, using the previously obtained singular value decomposition 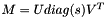 .
.
The solution is obtained with the following expression:
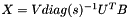 .
.
| U | input matrix U from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| s | input vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| V | input matrix V from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix |
Definition at line 224 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by solveBySingularValueDecomposition(), and solveFromSingularValueDecomposition().
| void solveFromSingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | U, | |
| const QVVector & | s, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | V, | |||
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained singular value decomposition
, using the previously obtained singular value decomposition 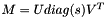 .
.
The solution is obtained with the following expression:
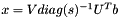 .
.
| U | input matrix U from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| s | input vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| V | input matrix V from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 241 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveBySingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the singular value decomposition
, using the singular value decomposition 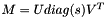 .
.
The solution is obtained by computing the singular value decomposition of 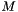 :
:
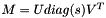
And then using the following expression
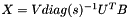 .
.
Being 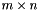 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 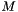 :
:
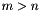 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 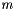 equations.
equations.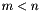 ), the obtained solution has minimum norm amongst all the valid solutions.
), the obtained solution has minimum norm amongst all the valid solutions.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| method | method to use in the SVD computation (see TQVSVD_Method) |
Definition at line 260 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveBySingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the singular value decomposition
, using the singular value decomposition 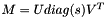 .
.
The solution is obtained by computing the singular value decomposition of 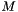 :
:
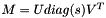
And then using the following expression
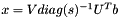 .
.
Being 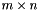 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 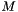 :
:
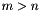 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 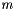 equations.
equations.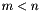 ), the obtained solution has minimum norm amongst all the valid solutions.
), the obtained solution has minimum norm amongst all the valid solutions.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 250 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by QVMatrix::matrixDivide().
| void solveBySingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| QVVector & | s, | |||
| QVMatrix & | V, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the singular value decomposition
, using the singular value decomposition 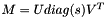 .
.
The solution is obtained by computing the singular value decomposition of 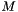 :
:
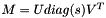
And then using the following expression
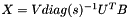 .
.
The function also returns the matrices 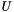 and
and 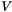 , and the vector
, and the vector 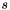 resulting from the singular value decomposition.
resulting from the singular value decomposition.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| U | param to store the matrix U resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| s | param to store the vector s resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| V | param to store the matrix V resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 280 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveBySingularValueDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| QVVector & | s, | |||
| QVMatrix & | V, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the singular value decomposition
, using the singular value decomposition 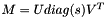 .
.
The solution is obtained by computing the singular value decomposition of 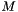 :
:
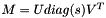
And then using the following expression
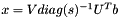 .
.
The function also returns the matrices 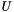 and
and 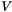 , and the vector
, and the vector 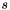 resulting from the singular value decomposition.
resulting from the singular value decomposition.
| M | input coefficient vector | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector | |
| U | param to store the matrix U resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| s | param to store the vector s resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| V | param to store the matrix V resulting from the singular value decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 269 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| double singularValueDecompositionResidual | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| const QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| const QVVector & | s, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | V | |||
| ) |
Checks for correctness of the SVD of a matrix.
This function computes the value 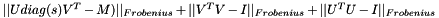 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 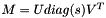 is a correct SVD of matrix M.
is a correct SVD of matrix M.
| M | input M matrix | |
| U | input U matrix from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| s | input vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition of M | |
| V | input V matrix from the SVD decomposition of M |
Definition at line 287 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void singularValues | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | s, | |||
| const TQVSV_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSV_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Gets the singular values of a matrix.
This function computes only the singular values of a matrix (which, depending on the used method, will be much faster than performing a full decomposition).
| M | input M matrix | |
| s | vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the SV computation (see TQVSV_Method) |
Definition at line 304 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the singular values of a matrix.
This function computes the value  , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 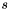 are the singular values of M.
are the singular values of M.
| M | input M matrix | |
| s | input vector of singular values from the SVD decomposition of M |
Definition at line 321 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void CholeskyDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const TQVCholesky_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the Cholesky decomposition of a symmetric and positive definite matrix.
The Cholesky decomposition obtains a lower triangular matrix L with strictly positive diagonal entries from an original matrix M, satisfying the following equation:
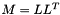
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| L | param to store the resulting matrix L from the Cholesky decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVCholesky_Method) |
Definition at line 382 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition
, using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition 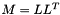 .
.
The matrix 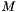 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 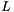 and
and 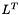 are solved by back-substitution to solve the linear system.
are solved by back-substitution to solve the linear system.
| L | input matrix from the Cholesky decomposition of M | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix |
Definition at line 387 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by solveByCholeskyDecomposition(), and solveFromCholeskyDecomposition().
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition
, using the previously obtained Cholesky decomposition 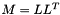 .
.
The matrix 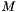 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 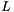 and
and 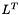 are solved by back-substitution to solve the linear system.
are solved by back-substitution to solve the linear system.
| L | input matrix from the Cholesky decomposition of M | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 394 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByCholeskyDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| const TQVCholesky_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the Cholesky decomposition
, using the Cholesky decomposition 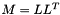 .
.
The matrix 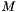 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 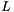 and
and 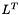 are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| method | method to use in the SVD computation (see TQVCholesky_Method) |
Definition at line 403 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by optimizeReprojectionErrorFor3DPoint(), optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPose(), optimizeReprojectionErrorForCameraPoseCauchy(), and sparseSolve().
| void solveByCholeskyDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| const TQVCholesky_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the Cholesky decomposition
, using the Cholesky decomposition 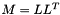 .
.
The matrix 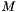 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 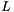 and
and 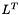 are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown vector x.
are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown vector x.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 412 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByCholeskyDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const TQVCholesky_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the Cholesky decomposition
, using the Cholesky decomposition 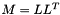 .
.
The matrix 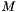 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 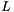 and
and 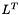 are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
The matrix 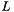 resulting from the Cholesky decomposition is also returned.
resulting from the Cholesky decomposition is also returned.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the Cholesky decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 422 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByCholeskyDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const TQVCholesky_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVCHOLESKY_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the Cholesky decomposition
, using the Cholesky decomposition 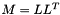 .
.
The matrix 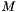 must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on
must be a symmetric positive definite matrix. The two resultant triangular systems on 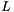 and
and 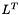 are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
are solved by back-substitution to obtain the unknown matrix X.
The matrix 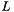 resulting from the Cholesky decomposition is also returned.
resulting from the Cholesky decomposition is also returned.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the Cholesky decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 430 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the Cholesky decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 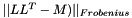 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 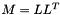 is a correct Cholesky decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct Cholesky decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| L | input matrix from the Cholesky decomposition of M |
Definition at line 441 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void LUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | P, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the LU decomposition of a rectangular  matrix.
matrix.
The LU decomposition obtains three matrices: P L, and U from an original matrix M, satisfying the following equation:
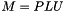
Being the original matrix M of size  , result matrices L and U are lower and upper triangular matrices of sizes
, result matrices L and U are lower and upper triangular matrices of sizes 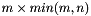 and
and 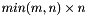 respectively, while P is a square
respectively, while P is a square 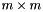 permutation matrix (in which each row and column have one and only one value equal to one, the rest of values being zeros).
permutation matrix (in which each row and column have one and only one value equal to one, the rest of values being zeros).
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| P | param to store the matrix P resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| U | param to store the matrix U resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVLU_Method) |
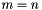 ) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular
) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular  matrices.
matrices.Definition at line 552 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by determinant().
| void solveFromLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | P, | |
| const QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained LU decomposition of M:
, using the previously obtained LU decomposition of M:
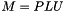
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 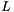 and
and 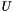 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 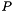 .
.
| P | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| L | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| U | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix |
Definition at line 557 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by solveByLUDecomposition(), and solveFromLUDecomposition().
| void solveFromLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | P, | |
| const QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained LU decomposition
, using the previously obtained LU decomposition 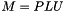 .
.
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 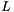 and
and 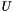 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 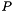 .
.
| P | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| L | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| U | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 578 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the LU decomposition
, using the LU decomposition 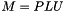 .
.
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 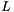 and
and 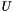 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 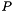 .
.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| method | method to use in the LU decomposition (see TQVLU_Method) |
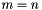 ) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular
) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular  system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense.
system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense. Definition at line 587 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the LU decomposition
, using the LU decomposition 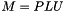 .
.
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 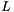 and
and 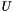 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 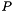 .
.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector | |
| method | method to use in the LU decomposition (see TQVLU_Method) |
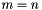 ) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular
) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular  system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense.
system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense. Definition at line 595 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| QVMatrix & | P, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the LU decomposition
, using the LU decomposition 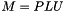 .
.
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 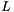 and
and 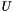 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 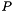 .
.
The function also returns the matrices 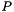 ,
, 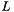 , and
, and 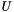 resulting from the LU decomposition.
resulting from the LU decomposition.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| P | param to store the matrix P resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| U | param to store the matrix U resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the LU decomposition (see TQVLU_Method) |
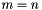 ) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular
) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular  system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense.
system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense. Definition at line 605 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByLUDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| QVMatrix & | P, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| QVMatrix & | U, | |||
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the LU decomposition
, using the LU decomposition 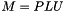 .
.
The solution for the linear system is obtained by solving the two resultant triangular systems on 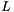 and
and 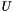 by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to
by back-substitution, while permuting the elements according to 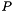 .
.
The function also returns the matrices 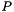 ,
, 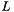 , and
, and 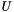 resulting from the LU decomposition.
resulting from the LU decomposition.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector | |
| P | param to store the matrix P resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| U | param to store the matrix U resulting from the LU decomposition (overwritten on output) |
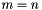 ) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular
) as input, otherwise it will fail and abort the program showing an adequate message. The LAPACK_DGETRF is more general, and accepts general rectangular  system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense.
system, if m<n (sub-determined). In this case, the solution vector obtained has n-m zeros in the last n-m positions. LU decomposition is not adequate in any case for solving overdetermined systems of equations (m>n). Use solveBySingularValueDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, TQVSVD_Method) or solveByQRDecomposition(const QVMatrix &, QVMatrix &, const QVMatrix &, const TQVQR_Method) instead for solving this type of systems in the minimum squares sense. Definition at line 613 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| double LUDecompositionResidual | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| const QVMatrix & | P, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | U | |||
| ) |
Checks for correctness of the LU decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 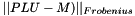 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 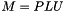 is a correct LU decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct LU decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| P | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| L | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M | |
| U | input matrix from the LU decomposition of M |
Definition at line 624 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void QRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the QR decomposition of a rectangular  matrix.
matrix.
The QR decomposition obtains two matrices Q and R from an original matrix M of size  that satisfy the following equation:
that satisfy the following equation:
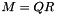
For a square matrix M (m=n), Q is orthogonal and R is upper triangular, both square of size 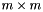 =
= 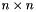 .
.
For full decomposition methods, or if m<n, matrix Q is orthogonal of size 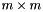 and R is an upper triangular matrix of size
and R is an upper triangular matrix of size  .
.
For thin decomposition methods, and if m>n, matrix Q has size  , with orthogonal columns, and R is an upper triangular matrix of size
, with orthogonal columns, and R is an upper triangular matrix of size 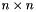 .
.
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| Q | param to store the resulting matrix Q from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| R | param to store the resulting matrix R from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVQR_Method) |
Definition at line 761 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the QR decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 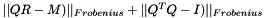 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 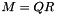 is a correct QR decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct QR decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| Q | input matrix from the QR decomposition of M | |
| R | input matrix from the QR decomposition of M |
Definition at line 766 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void QLDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the QL decomposition of a rectangular  matrix.
matrix.
The QL decomposition obtains two matrices Q and L from an original matrix M of size  that satisfy the following equation:
that satisfy the following equation:
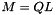
For a square matrix M (m=n), Q is orthogonal and L is lower triangular,both square of size 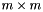 =
= 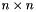 .
.
If m>n, then thin decomposition methods obtain a Q matrix of size  , with orthogonal columns, and a matrix L which is a lower triangular matrix of size
, with orthogonal columns, and a matrix L which is a lower triangular matrix of size 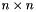 , while full decomposition methods obtain a matrix Q orthogonal of size
, while full decomposition methods obtain a matrix Q orthogonal of size 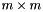 and a matrix L of size
and a matrix L of size  whose first m-n rows are zero, and whose last n rows form a lower triangular matrix.
whose first m-n rows are zero, and whose last n rows form a lower triangular matrix.
If m<n, then both full and thin decomposition methods obtain a matrix Q orthogonal of size 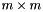 and a matrix L of size
and a matrix L of size  whose first m-n cols are in general not zero and whose last n columns form a lower triangular matrix.
whose first m-n cols are in general not zero and whose last n columns form a lower triangular matrix.
This function uses the underlying function QRDecomposition to perform the QL decomposition, so the available methods are the same than the ones used in the QR decomposition (see TQVQR_Method).
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| Q | param to store the matrix Q resulting from the QL decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the QL decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVQR_Method) |
Definition at line 771 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the QL decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 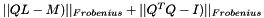 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 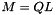 is a correct QL decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct QL decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| Q | input matrix from the QL decomposition of M | |
| L | input matrix from the QL decomposition of M |
Definition at line 784 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void RQDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the RQ decomposition of a rectangular  matrix.
matrix.
The RQ decomposition obtains two matrices R and Q from an original matrix M of size  that satisfy the following equation:
that satisfy the following equation:
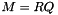
For a square matrix M (m=n), R is upper triangular and Q orthogonal, both square of size 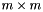 =
= 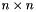 .
.
If m>n, then both full and thin decomposition methods obtain a matrix R of size  whose first m-n rows are in general not zero and whose last n rows form an upper triangular matrix, and a matrix Q which is orthogonal of size
whose first m-n rows are in general not zero and whose last n rows form an upper triangular matrix, and a matrix Q which is orthogonal of size 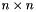 .
.
If m<n, then thin decomposition methods obtain a matrix R which is an upper triangular matrix of size 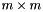 and a Q matrix of size
and a Q matrix of size  , with orthogonal rows, while full decomposition methods obtain a matrix R of size
, with orthogonal rows, while full decomposition methods obtain a matrix R of size  whose first n-m columns are zero, and whose last m columns form a lower triangular matrix, and a matrix Q orthogonal of size
whose first n-m columns are zero, and whose last m columns form a lower triangular matrix, and a matrix Q orthogonal of size 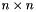 .
.
This function uses the underlying function QRDecomposition to perform the RQ decomposition, so the available methods are the same than the ones used in the QR decomposition (see TQVQR_Method).
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| R | param to store the matrix R resulting from the RQ decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| Q | param to store the matrix Q resulting from the RQ decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVQR_Method) |
Definition at line 789 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the RQ decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 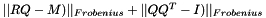 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 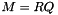 is a correct RQ decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct RQ decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| R | input matrix from the RQ decomposition of M | |
| Q | input matrix from the RQ decomposition of M |
Definition at line 802 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void LQDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | L, | |||
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the LQ decomposition of a rectangular  matrix.
matrix.
The LQ decomposition obtains two matrices L and Q from an original matrix M of size  that satisfy the following equation:
that satisfy the following equation:
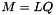
For a square matrix M (m=n), L is lower triangular and Q orthogonal, both square of size 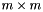 =
= 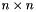 .
.
For full decomposition methods, or if m>n, L is a lower triangular matrix of size  and matrix Q is orthogonal of size
and matrix Q is orthogonal of size 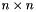 .
.
For thin decomposition methods, and if m<n, L is a lower triangular matrix of size 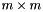 , and matrix Q has size
, and matrix Q has size  , with orthogonal rows.
, with orthogonal rows.
This function uses the underlying function QRDecomposition to perform the LQ decomposition, so the available methods are the same than the ones used in the QR decomposition (see TQVQR_Method).
| M | param containing the matrix to decompose | |
| L | param to store the matrix L resulting from the LQ decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| Q | param to store the matrix Q resulting from the LQ decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVQR_Method) |
Definition at line 807 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the LQ decomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 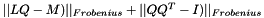 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 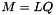 is a correct LQ decomposition of matrix M.
is a correct LQ decomposition of matrix M.
| M | input matrix | |
| L | input matrix from the LQ decomposition of M | |
| Q | input matrix from the LQ decomposition of M |
Definition at line 820 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveFromQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | Q, | |
| const QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M:
, using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M:
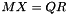
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 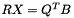 .
.
| Q | input matrix Q from the QR decomposition of M | |
| R | input matrix R from the QR decomposition of M | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix |
Definition at line 825 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by solveByQRDecomposition(), and solveFromQRDecomposition().
| void solveFromQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | Q, | |
| const QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M:
, using the previously obtained QR decomposition of M:
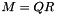
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 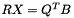 .
.
| Q | input matrix Q from the QR decomposition of M | |
| R | input matrix R from the QR decomposition of M | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 846 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the QR decomposition of M:
, using the QR decomposition of M:
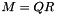
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 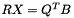 .
.
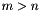 , being
, being 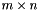 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 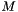 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 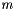 equations.
equations.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| method | method to use in the QR computation (see TQVQR_Method) |
Definition at line 864 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the QR decomposition of M:
, using the QR decomposition of M:
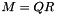
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 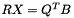 .
.
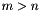 , being
, being 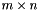 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 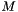 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 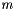 equations.
equations.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 855 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVMatrix & | X, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | B, | |||
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown matrix
for the unknown matrix  , using the QR decomposition of M:
, using the QR decomposition of M:
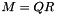
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 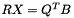 . The function also returns the matrices
. The function also returns the matrices 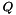 and
and 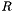 resulting from the QR decomposition.
resulting from the QR decomposition.
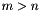 , being
, being 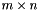 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 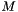 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 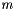 equations.
equations.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | unknown matrix (overwritten on output) | |
| B | input right hand side matrix | |
| Q | param to store the matrix Q resulting from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| R | param to store the matrix R resulting from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 882 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void solveByQRDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| QVMatrix & | R, | |||
| const TQVQR_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVQR_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves the linear system  for the unknown vector
for the unknown vector  , using the QR decomposition of M:
, using the QR decomposition of M:
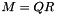
The solution is obtained by solving the triangular system 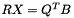 . The function also returns the matrices
. The function also returns the matrices 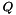 and
and 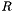 resulting from the QR decomposition.
resulting from the QR decomposition.
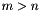 , being
, being 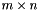 the size of the coefficient matrix
the size of the coefficient matrix 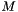 ), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the
), the obtained solution minimizes the sums of squares of the residuals of the 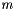 equations.
equations.| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | unknown vector (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right hand side vector | |
| Q | param to store the matrix Q resulting from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| R | param to store the matrix R resulting from the QR decomposition (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 872 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void eigenDecomposition | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | lambda, | |||
| QVMatrix & | Q, | |||
| const TQVEigenDecomposition_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVEIGENDECOMPOSITION_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the eigen-decomposition of a symmetric matrix.
The eigen-decomposition obtains the factorization of a symmetric matrix M into a canonical form, represented in terms of a set of eigenvectors and their corresponding eigenvalues.
Each eigenvector 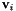 and its corresponding eigenvalue
and its corresponding eigenvalue 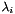 satisfy the following equation.
satisfy the following equation.

This function returns the eigenvectors and their corresponding eigenvalues in a Q matrix and a lambda vector, respectively. Each eigenvector is stored as a row of the Q matrix. The i-th element of the vector lambda contains the eigenvalue corresponding to the eigenvector stored in the i-th row. Eigenvectors are mutually orthogonal, therefore, Q is an orthonormal matrix (i.e. 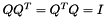 )
)
Thus, the following equation holds, given that the matrix 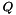 and the vector
and the vector 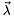 contain respectively the eigen-vectors and the eigen-values of the symmetric matrix M:
contain respectively the eigen-vectors and the eigen-values of the symmetric matrix M:
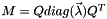
| M | symmetric matrix to obtain eigen-decomposition | |
| lambda | vector containing the eigenvalues from the eigen-decomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| Q | matrix containing the eigenvectors from the eigen-decomposition of M; eigenvectors are stored as row vectors (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVEigenDecomposition_Method) |
Definition at line 990 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| double eigenDecompositionResidual | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| const QVVector & | lambda, | |||
| const QVMatrix & | Q | |||
| ) |
Checks for correctness of the eigendecomposition of a matrix.
This function computes the value 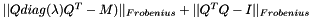 , which should be close to zero if
, which should be close to zero if 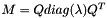 is a correct eigendecomposition of symmetric matrix M.
is a correct eigendecomposition of symmetric matrix M.
| M | input symmetric M matrix | |
| lambda | input vector of eigenvalues from the eigendecomposition of M | |
| Q | input Q matrix from the eigendecomposition of M |
Definition at line 995 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| void eigenValues | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | lambda, | |||
| const TQVEigenValues_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVEIGENVALUES_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Gets the eigenvalues of a matrix.
This function computes only the eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix (which, depending also on the used method, will be much faster than performing a full eigendecomposition).
| M | input symmetric M matrix | |
| lambda | vector of eigenvalues from the eigendecomposition (overwritten on output) | |
| method | method to use in the eigenvalues computation (see TQVEigenValues_Method) |
Definition at line 1008 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Checks for correctness of the eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix.
This function returns the difference between the sum of diagonal elements of the matrix (i.e., its trace) and the sum of the elements of 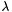 (which are supposed to be its eigenvalues). This should be close to zero if the
(which are supposed to be its eigenvalues). This should be close to zero if the 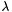 are really the eigenvalues of M.
are really the eigenvalues of M.
| M | input M matrix | |
| lambda | input vector of eigenvalues from the eigendecomposition of M |
Definition at line 1020 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| QVMatrix pseudoInverse | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD, |
|||
| const double | epsilon = 1.0E-10 | |||
| ) |
Obtains the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse of a matrix.
The pseudoinverse is computed using the SVD of the input matrix, and then using the reciprocal of the obtained singular values. The used formula is 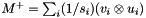 , being
, being 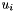 and
and 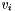 column vectors of the orthogonal U and V matrices obtained by SVD. Singular values which, when divided by the first singular value, are smaller than the epsilon parameter are discarded in the computation.
column vectors of the orthogonal U and V matrices obtained by SVD. Singular values which, when divided by the first singular value, are smaller than the epsilon parameter are discarded in the computation.
| A | input matrix to obtain pseudoinverse | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVSVD_Method) | |
| epsilon | singular values with value smaller than epsilon will be discarded in computation |
Definition at line 1037 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by computeAffineHomography(), correctIntrinsics(), QVMatrix::inverse(), linearCameraCenterResection(), and qvLinearRegularizedRegression().
| double determinant | ( | const QVMatrix & | M, | |
| const TQVLU_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVLU_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Obtains the determinant of a square matrix.
The determinant is obtained by first obtaining the LU decomposition of the matrix, then multiplying the values in the diagonal of U, and finally multiplying the result by the signature of the permutation P in the decomposition 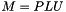
| M | matrix to obtain the determinant | |
| method | method to use in the LU decomposition (see TQVLU_Method) |
Definition at line 1057 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by QVMatrix::det(), getCameraPosesFromEssentialMatrix(), and QVEuclideanMapping3::QVEuclideanMapping3().
| void solveHomogeneous | ( | const QVMatrix & | A, | |
| QVector< double > & | x, | |||
| const TQVSVD_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSVD_METHOD | |||
| ) |
Solves an homogeneous linear system of equations.
Given a matrix M, this functions obtain the vector x satisfying the following equation:
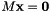
The solution is based on the SVD decomposition of the matrix A. Vector x is set to the last column of the matrix V from the SVD decomposition of M.
| M | coeficient matrix for the homogeneous equation system. | |
| x | vector to store the solution. | |
| method | method to use in the SVD decomposition (see TQVSVD_Method) |
Definition at line 1092 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by linear3DPointTriangulation(), and linearCameraResection().
Returns the residual of the solution to a linear matrix equation.
This function computes the value 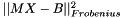 , which should be close to zero if X is the solution to the matrix equation
, which should be close to zero if X is the solution to the matrix equation 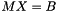 , or should be minimized if the system was solved in the minimum squares sense.
, or should be minimized if the system was solved in the minimum squares sense.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| X | input unknown matrix | |
| B | input right hand side matrix |
Definition at line 1101 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Returns the residual of the solution to a linear vector equation.
This function computes the value 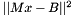 , which should be close to zero if x is the solution to the equation
, which should be close to zero if x is the solution to the equation 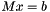 , or should be minimized if the system was solved in the minimum squares sense.
, or should be minimized if the system was solved in the minimum squares sense.
| M | input coefficient matrix | |
| x | input unknown vector | |
| b | input right hand side vector |
Definition at line 1108 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
| double sparseSolve | ( | const QVSparseBlockMatrix & | M, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const QVVector & | b, | |||
| const bool | isSymmetric = false, |
|||
| const bool | isPosDefinite = false, |
|||
| const TQVSparseSolve_Method | method = DEFAULT_TQVSPARSESOLVE_METHOD, |
|||
| const bool | start_from_x = false, |
|||
| const bool | iters_or_resid = true, |
|||
| const int | iters = 0, |
|||
| const double | resid = 1.0E-10, |
|||
| int & | final_iter_count = dummy | |||
| ) |
Solves a sparse system of linear equations, taking advantage of sparseness to accelerate the computation.
Given a coefficient matrix M and an objective vector b, this functions obtains the vector x satisfying the following equation:
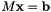
| M | input coeficient sparse block matrix in the matrix equation form of the problem (must be square) | |
| x | vector to store the solution (overwritten on output) | |
| b | input right-hand side vector in the matrix equation form of the problem | |
| isSymmetric | indicates if M must be considered symmetric (in this case, only the upper triangular part is taken into account, which will speed up the computation). | |
| isPosDefinite | indicates if M is positive definite (in this case, the solver will take this into account to speed up the computation). | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVSparseSolve_Method) | |
| start_from_x | only for the QVMKL_ISS method, if true, start from the input value of x | |
| iters_or_resid | only for the QVMKL_ISS method, if true, use max iterations termination test (see param iters), otherwise use max residual (see param max_resid) | |
| iters | only for the incremental methods (QVMKL_ISS and QV_SCG). Number of iterations to execute (if zero, iterate until convergence or error) | |
| max_resid | only for the incremental methods (QVMKL_ISS and QV_SCG). Iterate until square of residual is below this parameter | |
| iters | only for the QVMKL_ISS method, final number of iterations really executed (overwritten on output) |
Definition at line 1216 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.
Referenced by globalEpipolarAdjustment(), and incrementalGEA().
| bool solveHomogeneous | ( | const QVSparseBlockMatrix & | A, | |
| QVVector & | x, | |||
| const int | maxIterations = 10, |
|||
| const double | minRelativeError = 0.0, |
|||
| const TQVSparseSolve_Method | method = QVMKL_DSS | |||
| ) |
Solves a sparse homogeneous linear system using the inverse iteration algorithm and the MKL sparse routines.
Given a matrix M, this function obtains the vector x satisfying the following equation:
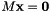
An iterative process is used to converge from an initial random solution to the optimal solution of the equation.
| M | input coeficient sparse block matrix in the matrix equation form of the problem (must be square) | |
| x | this vector will contain the solution to the homogeneous linear system in return. An initial approximation to the solution can be provided in this argument. | |
| maxIterations | number of maximal iterations to perform in the algoritm. | |
| minRelativeError | the iteration process will stop if the value 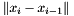 (the difference between the solutions obtained in the last two iterations) is smaller than this value. (the difference between the solutions obtained in the last two iterations) is smaller than this value. | |
| method | method to use in the computation (see TQVSparseSolve_Method). Only method QVMKL_DSS is currently implemented for this function. |
Definition at line 1629 of file qvmatrixalgebra.cpp.